13rd September 2022, NIA Diagnostic Imaging

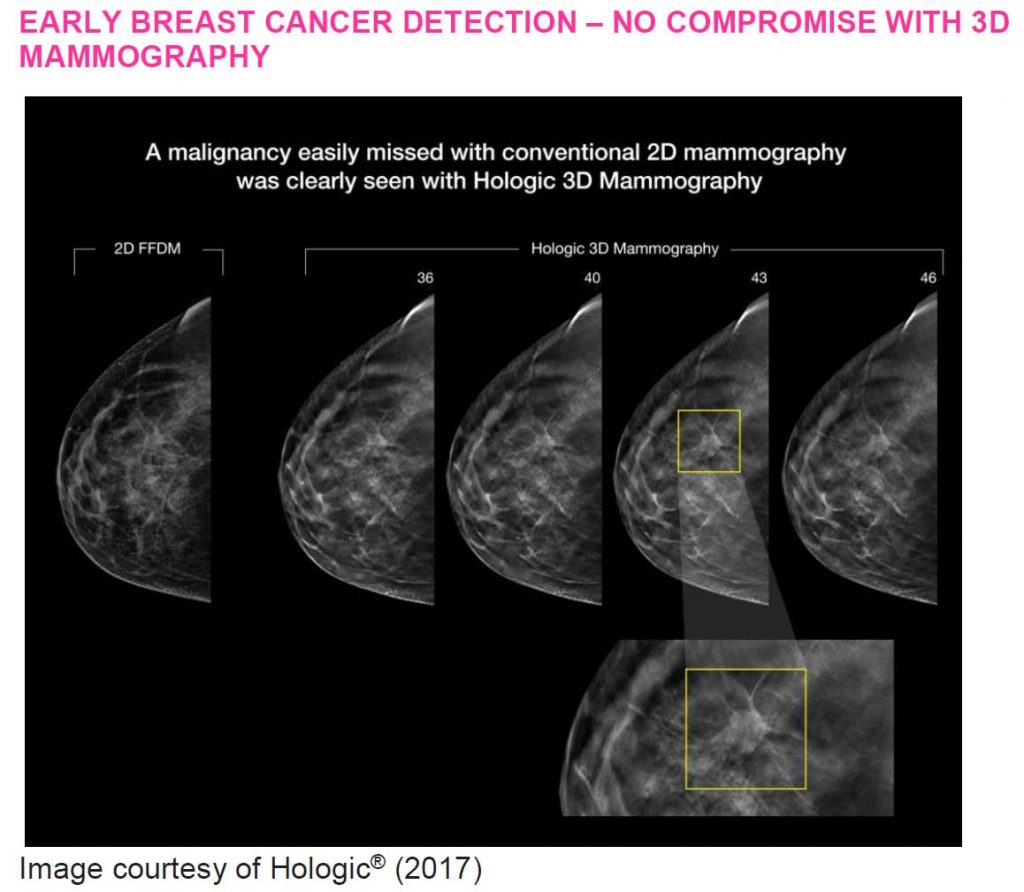
Mammography remains the gold standard imaging technique in early-stage breast cancer diagnosis. It forms part of the triple test approach to the investigation of new breast symptoms. (Cancer Australia 2021). In the past, there used to be limitations with conventional mammography’s sensitivity and specificity in detecting abnormalities in young female breasts due to the patients’ mostly dense breast tissues. This has now been greatly improved with the use of digital breast tomosynthesis or also called 3D mammography technique.
Digital breast tomosynthesis allows radiologists to view breast images in multiple layers or slices of otherwise overlapping breast tissues, which enables not only higher cancer detection rate, but also more confident characterisations of benign lesions. In fact, results from Friedewald et al. (2014)’s study has found an average of 20-65% increase in invasive breast cancers detected per 1000 screening exams in women receiving the combined 2D and 3D mammograms acquired with the Hologic® 3D Mammography™ system, as compared with those receiving 2D mammogram alone.
The use of digital breast tomosynthesis also accounts for up to 40% reduction in recalls compared with the conventional 2D mammography alone. Subsequently, one can say that 3D mammogram helps speed up reporting process and avoid long result waiting time, which in turn may reduce patient’s anxiety. From the managing clinician’s point of view, the prompt availability of imaging results means that core biopsy and/or fine needle aspiration (FNA) of breast lesions can be requested without delay, facilitating disease diagnosis and treatment plan. Overall, breast imaging using 3D mammogram +/- ultrasound in all age groups have proven to be very effective tools in breast cancer diagnosis, particularly in (young) women with dense breasts.
This state-of-the-art technology, powered by Hologic® the global industry leader in breast heath, is readily available at NIA Diagnostic Imaging. With a team of experienced mammographers, sonographers and radiologists on site, NIA Diagnostic Imaging can collaborate with the managing clinicians to deliver a seamless diagnosis journey for patients, from 3D mammography, ultrasound to imaging guided biopsy.
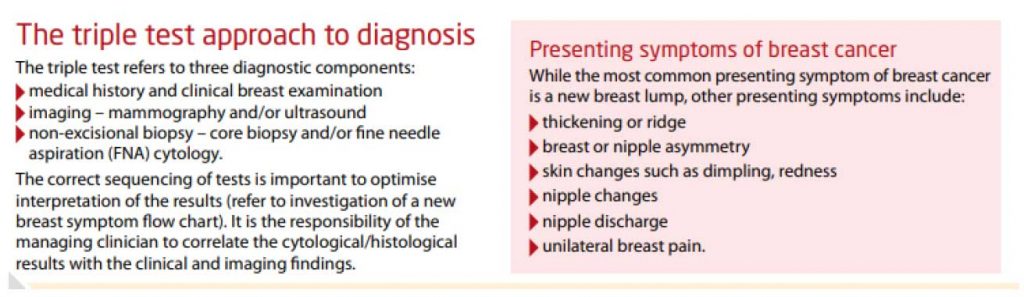
Mammography is just one facet of the triple test approach to the diagnosis.
According to Cancer Australia, breast cancer is the second most commonly diagnosed cancer in Australia in 2022. Approximately 57 Australians (both females and males) are diagnosed each and every day, which equates to over 20,000 breast cancer cases each year. (National Breast Cancer Foundation, 2022). About 1 in 600 men are diagnosed with breast cancer in their lifetime and about 1 in 7 women are diagnosed in their lifetime. As age is one of the risk factors, women between the ages of 50-74 are currently being invited for annual screening mammograms. However, it is also worth noted that around 1000 young women are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, equivalent to about 3 young women each day. Statistics has shown that in 2022, approximately one woman under the age of 40 is expected to die each week from breast cancer. (National Breast Cancer Foundation, 2022) This highlights the importance of accurate and early breast cancer diagnosis in young female patients in order to improve their prognosis.

References:
- Cancer Australia 2022, Breast Cancer, viewed 10 September 2022, https://www.canceraustralia.gov.au/cancer-types/breast-cancer/statistics
- National Breast Cancer Foundation 2022, Breast Cancer Stats, viewed 10 September 2022, https://nbcf.org.au/about-breast-cancer/breast-cancer-stats/#:~:text=Around%201000%20young%20women%20are,each%20week%20from%20breast%20cancer
- Cancer Australia 2022, The Investigation of A New Breast Symptom, A Guide for General Practitioners, viewed 10 September 2022, https://www.canceraustralia.gov.au/sites/default/files/publications/investigation-new-breast-symptom-guide-general-practitioners/pdf/investigation-of-a-new-breast-symptom-a-guide-for-general-practitioners.pdf
- Friedewald SM et al. 2014, ‘Breast cancer screening using tomosynthesis in combination with digital mammography’, JAMA vol 311, no. 24. pp.2499-2507.
- Finding Value in Digital Breast Tomosynthesis 2017, Imaging Technology News, viewed 10 September 2022, https://www.itnonline.com/article/finding-value-digital-breast-tomosynthesis
