13th August 2025, A/Prof Chee L Khoo
We know the ongoing cost and availability of anti-obesity medications (AOM) the likes of Wegovy and Mounjaro although we have been assured that the supply issue is behind us now. Part of the problem with cost relate to the manufacturing cost of the devices. In fact, the rate limiting step to the production is the pen, which needs to be precisely manufactured and tested as it is a medical device. This is also a reason why disposable pens in our insulin devices have been phased out to divert pen manufacturing to the AOM. One solution is to create AOM in an oral form. A major problem obviously is that GLP1-RA is a peptide which needs to modified to survive the gastric juices. Semaglutide people have done it. We already have Rybelsus® approved by the TGA in 2022. There is another novel solution to the problem, though.
Orforglipron is a small-molecule, non-peptide GLP1-RA affecting the activity of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). Its mimics the actions of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) for reducing food intake and lowering blood glucose levels. There have been other -gliprons developed (danuglipron and lotiglipron) but have been withdrawn due to liver toxicities. Orforglipron just released its results from the ACHIEVE-1 and ATTAIN-1 trials demonstrating safety and efficacy in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and obesity respectively.
ACHIEVE-1
This is a phase 3, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial where 559 patients with T2D treated with diet and exercise with HbA1c between 7-9.5% and BMI > 23 were randomly assigned to receive orforglipron at one of three doses (3 mg, 12 mg, or 36 mg) or placebo once daily for 40 weeks (1). The primary end point was the change from baseline to week 40 in the HbA1c level. A key secondary end point was the percent change in body weight.
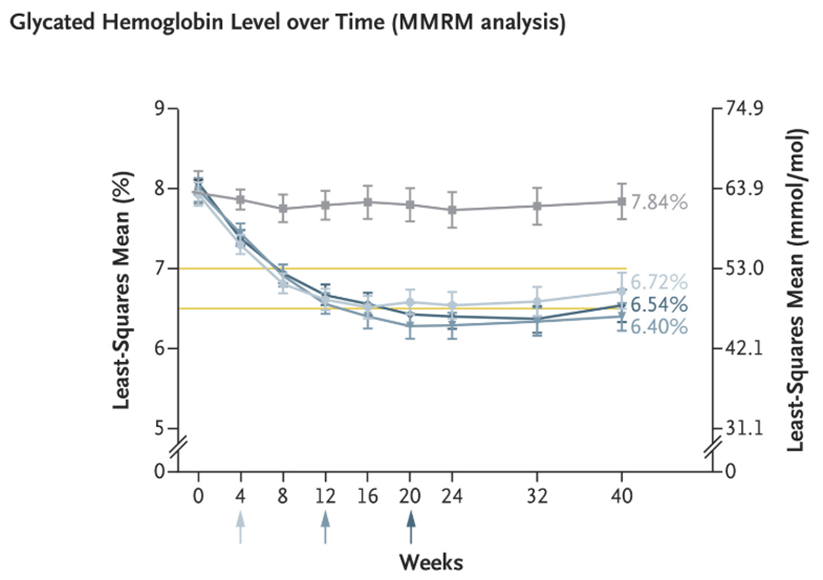
The mean change from baseline in the HbA1c level was −1.24 percentage points with the 3-mg dose, −1.47 percentage points with the 12-mg dose, −1.48 percentage points with the 36-mg dose, and −0.41 percentage points with placebo. The percent change in body weight from baseline to week 40 was −4.5% with the 3-mg dose, −5.8% with the 12-mg dose, −7.6% with the 36-mg dose, and −1.7% with placebo. (See Figure 1). The most common adverse events were mild-to-moderate gastrointestinal events, most of which occurred during dose escalation. No episodes of severe hypoglycaemia were reported.
ATTAIN-1
This trial just released their topline results a week ago. The full results is yet to be published. 3,127 adults with obesity, or overweight with a weight-related medical problem and without diabetes were randomised to the three doses of orforglipron (3mg, 12mg, 36mg) or placebo (2). At 72 weeks, the maximal dose of orforglipron (36 mg) lowered weight by an average of 12.4% compared to 0.9% with placebo. In addition to achieving significant weight loss, orforglipron was also associated with reductions in known markers of cardiovascular risk, including non-HDL cholesterol, triglycerides and systolic blood pressure in pooled analyses across all doses. In a pre-specified exploratory analysis, the highest dose of orforglipron reduced high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) levels by 47.7%. The most commonly reported adverse events were gastrointestinal-related and generally mild-to-moderate in severity.
The full results will be unveiled at the Vienna EASD meeting in a month’s time. I will be keeping an eye on the results.
Wow. Orforglipron is the first oral GLP1-like agent to demonstrate efficacy in Hba1c reduction and weight reduction but is certainly not the first oral GLP1 agent to do so.
In the PIONEER trial way back in 2019, oral semaglutide monotherapy (3, 7, 14mg) demonstrated superior and clinically relevant improvements in HbA1c (-0.6% to -1.4%-) and body weight loss (-0.2mg to -2.6kg) versus placebo, with a safety profile consistent with other GLP-1 receptor agonists (3).
Using a much bigger dose, in the OASIS 1 trial, once daily oral semaglutide 50mg resulted in a -15.1% reduction in body weight from baseline after 68 weeks compared with -2.4% with placebo (4). Gastrointestinal adverse events (mostly mild to moderate) were reported in 268 (80%) participants with oral semaglutide 50 mg and 154 (46%) with placebo.
In the SOUL trial (Semaglutide cardiOvascular oUtcomes trial) just published in May 2025, 9650 participants 50 years of age or older who had T2D with a HbA1c of 6.5 to 10.0%, and had known atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, or both to receive either once-daily oral semaglutide (maximal dose, 14 mg) or placebo, in addition to standard care (5). After a mean follow-up of 49.5 months, the oral semaglutide group 12% of participants suffered major adverse cardiovascular events compared with 13.8% in the standard care group (a significant 14% reduction).
Oral GLP1-RAs, peptides or non-peptides have now been shown to be beneficial in glycaemic control, weight reduction and cardiovascular outcomes (at least in oral semaglutide). They are less potent than their injectable counterparts but certainly should be cheaper to manufacture which hopefully translate to cheaper to purchase. Oral semaglutide is already approved by the TGA but I understand that there are logistical issues on how and when to take the tablets which is delaying its launch in Australia. The orforglipron people suggest that it will be available within the next 12-15 months. Watch this space.
References:
- Rosenstock J, Hsia S, Nevarez Ruiz L, Eyde S, Cox D, Wu WS, Liu R, Li J, Fernández Landó L, Denning M, Ludwig L, Chen Y; ACHIEVE-1 Trial Investigators. Orforglipron, an Oral Small-Molecule GLP-1 Receptor Agonist, in Early Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2025 Jun 21.
- https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/news-release-details/lillys-oral-glp-1-orforglipron-delivers-weight-loss-average-273 Accessed 13/08/2025
- Aroda VR, Rosenstock J, Terauchi Y, Altuntas Y, Lalic NM, Morales Villegas EC, Jeppesen OK, Christiansen E, Hertz CL, Haluzík M; PIONEER 1 Investigators. PIONEER 1: Randomized Clinical Trial of the Efficacy and Safety of Oral Semaglutide Monotherapy in Comparison With Placebo in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2019 Sep;42(9):1724-1732.
- Knop FK, Aroda VR, do Vale RD, Holst-Hansen T, Laursen PN, Rosenstock J, Rubino DM, Garvey WT; OASIS 1 Investigators. Oral semaglutide 50 mg taken once per day in adults with overweight or obesity (OASIS 1): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2023 Aug 26;402(10403):705-719
- McGuire DK, Marx N, Mulvagh SL, Deanfield JE, Inzucchi SE, Pop-Busui R, Mann JFE, Emerson SS, Poulter NR, Engelmann MDM, Ripa MS, Hovingh GK, Brown-Frandsen K, Bain SC, Cavender MA, Gislum M, David JP, Buse JB; SOUL Study Group. Oral Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in High-Risk Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2025 May 29;392(20):2001-2012.
